In the 1990s, the first spine navigation systems were introduced. They represented a true revolution, assisting surgeons during screw placement by providing more information and therefore greater safety. Many years passed before robotic systems and other advanced technologies appeared, and only quite recently did this market begin to develop significantly.
However, technological innovation continues to advance, and an increasing number of devices and solutions are now available. In recent years, some companies have developed what is known as augmented reality (AR). This technology supports and complements the surgeon by eliminating the need to divert attention to navigation screens. Instead, through smart glasses or a dedicated device, the surgeon can view both the surgical field and the information provided by the navigation system at the same time.
What does AR contribute to spine surgery?
AR offers several advantages compared to traditional surgical navigation methods:
- Simultaneous visualization of real anatomy and 3D navigation data
- Enables planning and instrument guidance without diverting attention from the operative field
- Reduces dependence on intraoperative radiation (by decreasing the need for repeated fluoroscopy)
- May improve accuracy in procedures such as pedicle screw placement in spinal fusion
- Reduces cognitive load and may shorten surgical time and surgeon fatigue (augmedics.com)
In preliminary studies, AR systems have shown high rates of accurate screw placement, with reductions in radiation exposure and a shorter learning curve compared with traditional navigation methods (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
What are the main AR systems in spine surgery?
1.-Augmedics – xvision Spine System
One of the pioneering and most widely adopted augmented reality systems in clinical practice. It allows the surgeon to visualize the patient’s 3D anatomy and instrument trajectories directly within the field of view, providing an experience similar to having “X-ray vision”. MeetX2 VIDEO ANIMATION
Key strengths
High clinical penetration, strong regulatory validation, and published studies demonstrating improvements in accuracy and surgical ergonomics.
2.-Globus Medical – Excelsius XR Extended Reality Navigation
An extended reality (XR) navigation headset developed by Globus Medical that enhances surgical visualization and control. It integrates with the existing Excelsius navigation ecosystem, allowing the surgeon to view 2D data and 3D anatomical models while maintaining direct line of sight on the patient. Excelsius XR also includes intuitive hand-tracking control and can work alongside other Excelsius systems such as ExcelsiusHub and Excelsius3D. Excelsius XR VIDEO ANIMATION
Key strengths
Offers hands-free control and simultaneous visualization of anatomy and navigation data, improving workflow continuity and reducing the need to look away from the surgical field.
3.-OnPoint Augmented Reality Spine System
OnPoint Surgical has developed an advanced augmented reality (AR) navigation system for spine surgery that projects virtual surgical guides and virtual implants directly onto the patient in the surgeon’s visual field using a see‑through optical head‑mounted display. It is intended to improve accuracy, hand‑eye coordination, and surgical workflow while preserving tactile feedback and maintaining current surgical technique. OnPoint VIDEO ANIMATION
Key strengths
The OnPoint AR Spine System’s key strengths include FDA 510(k) clearance for clinical use, real-time 3D visualization of anatomical landmarks and planned trajectories, and compatibility with implants from major manufacturers without altering surgical techniques. Preclinical studies demonstrate 2–5× higher accuracy than existing navigation, robotic, and AR systems, while its lightweight, high-resolution design and small footprint make it suitable for both hospital operating rooms and ambulatory surgery centers.
4.-Philips – ClarifEye Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation
ClarifEye is an augmented reality (AR) surgical navigation system developed by Royal Philips to assist spine procedures, especially in hybrid operating rooms. It integrates imaging and real‑time AR guidance into a single platform to support accurate device and implant placement, such as pedicle screws during spinal fusion.
Key Strengths
ClarifEye’s key strengths include its integration of intraoperative 2D and 3D imaging with AR navigation in a single platform, providing live visual feedback and guidance during pedicle screw placement. It operates at low X‑ray doses while maintaining high image quality, reduces the need for repeat postoperative CT scans, and eliminates cumbersome reference frames used in other systems. Its adoption in hybrid ORs across multiple countries demonstrates its clinical viability and global applicability.
5.-Surglasses – Caduceus S AR Spine Navigation
An augmented reality system developed by Taiwan Main Orthopaedic Biotechnology Co., Ltd. that overlays 3D patient anatomy information onto the surgical field during spine procedures. Caduceus VIDEO ANIMATION
Key strengths:
Focuses on AR-based surgical navigation with an emphasis on reducing radiation and equipment footprint.
6.-Novarad – VisAR Augmented Reality Navigation
An augmented reality surgical navigation system designed to guide spine procedures by directly overlaying 3D imaging maps onto the patient through an AR headset.
Key strengths:
A combination of high accuracy, continuous data registration, and a reduced operating-room footprint.
7.-Brainlab – Spine Mixed Reality Navigation
A mixed reality navigation technology that combines advanced optical tracking with enhanced visualization directly within the surgeon’s field of view.
Key strengths:
Integration with traditional optical navigation systems and strong value for surgical education.
Summary Insights
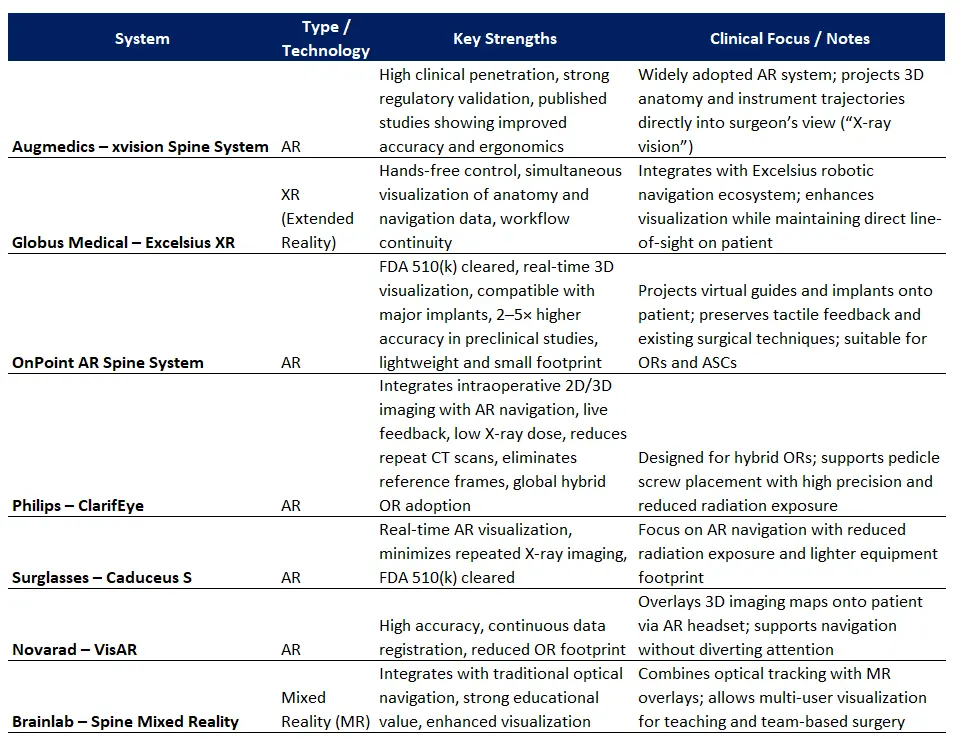
- Clinical maturity: xvision, Excelsius XR, OnPoint, and ClarifEye are FDA-cleared and widely used; Surglasses, VisAR, and Brainlab MR have regional or emerging adoption.
- Unique differentiators:
- xvision: pioneering AR “X-ray vision”
- Excelsius XR: integration with robotic guidance, XR headset
- OnPoint: high preclinical accuracy, open implant compatibility, lightweight
- ClarifEye: hybrid OR integration, low radiation, intraoperative imaging fusion
- Workflow advantages: AR/XR/MR systems all aim to keep surgeon attention on the patient, reduce cognitive load, improve precision, and in many cases reduce radiation exposure.
- Research & education: Brainlab MR and Novarad VisAR emphasize integration with training and teaching, as well as continuous data tracking.
Others: AR and Mixed-Reality Systems in Development and Research
There are ongoing academic projects and research prototypes exploring extended reality technologies for surgical assistance in spine and orthopedic surgery.
- These systems are using devices such as Magic Leap and Microsoft HoloLens to overlay 3D visualizations and guide surgical tools.
- Most are not yet clinically adopted but represent emerging directions for AR and XR assistance in surgery.
Opinion and Perspectives
Augmented reality (AR) in spine surgery has moved beyond the realm of futuristic prototypes, with multiple clinically validated systems now in use for hundreds or thousands of procedures, demonstrating improved accuracy, ergonomics, and reductions in radiation exposure and operative time. These technologies offer a more intuitive, patient-centered workflow, enhanced precision in delicate procedures, reduced cognitive load, and the potential to lower both radiation exposure and long-term costs.
However, challenges remain, including implementation and training expenses, integration with hospital infrastructure and digital operating rooms, and the need for larger multicenter studies to establish standardized clinical protocols. The AR/XR market for spine surgery is dynamic and competitive, with established systems from Augmedics, Globus Medical, Novarad, and Brainlab, alongside emerging innovators and startups leveraging platforms such as HoloLens, Magic Leap, and Arsoft, highlighting a rapidly evolving landscape with expanding solutions and clinical opportunities.
###
